Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) is a multifaceted neurodevelopmental condition that affects individuals of all ages. From its symptoms and potential causes to available treatments and emerging complementary approaches like Lion's Mane Mushroom, understanding ADHD in its entirety is crucial for effective management and support.

Understanding ADHD
ADHD is a neurodevelopmental disorder characterised by a persistent pattern of inattention, hyperactivity, and impulsivity that significantly impairs functioning and quality of life. It affects both children and adults, with symptoms often manifesting in childhood and persisting into adolescence and adulthood. ADHD can impact various domains of life, including academic and occupational performance, relationships, and emotional well-being.
Symptoms of ADHD
Inattention
Individuals with ADHD may struggle to sustain attention on tasks or activities, often becoming easily distracted by unrelated stimuli. They may make mistakes due to a lack of attention to details, leading to errors in work or school assignments.
Forgetfulness in daily activities is common, such as forgetting appointments, losing items, or failing to follow through on tasks.
Hyperactivity
Hyperactivity in individuals with ADHD manifests as a constant need for movement and restlessness, making it difficult to sit still for extended periods. They may have difficulty engaging in quiet leisure activities and may seek stimulation or movement to alleviate restlessness.
Excessive talking and a sense of being "on the go" are typical characteristics of hyperactivity in ADHD.
Impulsivity
Impulsivity in ADHD is characterised by hasty decision-making without considering the consequences. Individuals with ADHD may struggle to wait for their turn in situations that require patience, leading to impatience and frustration.
Interrupting or intruding on others' conversations or activities is common, as individuals with ADHD may struggle to control impulses.
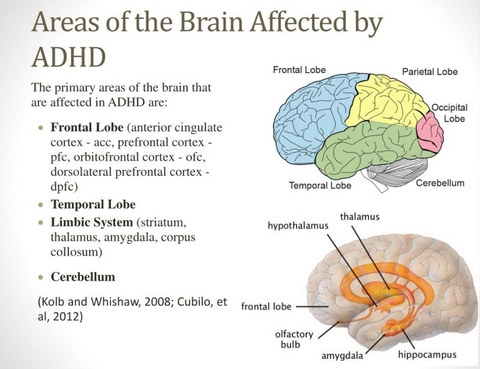
Reference: https://www.slideserve.com/swann/areas-of-the-brain-affected-by-adhd
Exploring the Causes of ADHD
Understanding the underlying causes of ADHD involves considering various factors, including genetic, neurobiological, environmental, and psychosocial influences:
Genetic Factors: ADHD often runs in families, suggesting a genetic predisposition. Studies have identified multiple genes associated with ADHD, although the interplay between genetics and environmental factors is complex.
Neurobiological Factors: Differences in brain structure and function, particularly involving neurotransmitter systems such as dopamine and norepinephrine, contribute to ADHD symptoms. Neuroimaging studies have shown alterations in brain regions involved in attention, impulse control, and executive function in individuals with ADHD.
Environmental Factors: Prenatal and perinatal factors, such as maternal smoking, alcohol consumption, exposure to environmental toxins, premature birth, and low birth weight, may increase the risk of developing ADHD. Adverse childhood experiences, including trauma, neglect, or chronic stress, can also exacerbate ADHD symptoms or contribute to comorbid conditions like anxiety or depression.
Treatment Approaches for ADHD
Managing ADHD typically involves a multimodal approach tailored to individual needs, preferences, and symptom severity:
Behavioural Therapy
Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy (CBT): Helps individuals develop coping strategies, improve organisational skills, and address maladaptive thought patterns related to ADHD symptoms.
Behavioural Interventions: Utilising reward systems, time management techniques, and environmental modifications to promote positive behaviour and reduce symptoms.
Medication
Stimulant Medications: Such as methylphenidate (e.g., Ritalin) and amphetamine (e.g., Adderall), are commonly prescribed to enhance attention, focus, and impulse control by increasing dopamine and norepinephrine levels in the brain.
Non-Stimulant Medications: Including atomoxetine (Strattera) and certain antidepressants (e.g., bupropion) may be recommended for individuals who do not respond well to stimulants or have concerns about their side effects.
Educational and Workplace Accommodations
Providing academic accommodations, such as extended time for exams, preferential seating, or access to assistive technology, can support students with ADHD in educational settings.
Workplace accommodations may include flexible scheduling, ergonomic workstations, and clear communication channels to enhance productivity and job performance.
Parental and Peer Support
Engaging in parent training programs and support groups can empower caregivers with effective parenting strategies and a supportive network of peers facing similar challenges.
Peer support groups for individuals with ADHD offer a sense of community, validation, and shared experiences, reducing feelings of isolation and stigma.
Lion's Mane Mushroom: A Potential Adjunctive Therapy for ADHD?
Lion's Mane Mushroom (Hericium erinaceus) is a unique fungus revered for its potential cognitive and neurological benefits. Traditionally used in Asian cuisine and herbal medicine, Lion's Mane Mushroom has gained popularity in recent years for its purported role in supporting brain health and cognitive function.
While research on Lion's Mane Mushroom's specific effects on ADHD is still emerging, its neuroprotective and cognitive-enhancing properties suggest potential benefits for individuals with ADHD.

Benefits of Lion's Mane Mushroom
Cognitive Enhancement
Lion's Mane Mushroom has been studied for its potential to enhance cognitive function, including memory, attention, and executive function. Some research suggests that Lion's Mane Mushroom may support neuroplasticity, the brain's ability to reorganise and form new neural connections, which could benefit individuals with ADHD.
Neuroprotection
Bioactive compounds in Lion's Mane Mushroom, such as hericenones and erinacines, exhibit neuroprotective effects, safeguarding neurons from damage caused by oxidative stress and inflammation.
Neuroregeneration
Some research suggests that Lion's Mane Mushroom may stimulate nerve growth factor (NGF) production, promoting neuroregeneration and synaptic plasticity in the brain. This could potentially support the development of neural circuits involved in attention, impulse control, and executive function, which are impaired in individuals with ADHD.
Functions of Bioactive Compounds in Lion's Mane Mushroom
Hericenones
Hericenones are aromatic compounds found in Lion's Mane Mushroom known for their neuroprotective and anti-inflammatory properties. They may help protect neurons from damage and reduce inflammation in the brain, which could benefit individuals with ADHD.
Erinacines
Erinacines are bioactive compounds with potential neuroregenerative effects, promoting the growth and differentiation of nerve cells. By stimulating nerve growth and repair, erinacines may support cognitive function and neural plasticity in individuals with ADHD.
Beta-Glucans
Lion's Mane Mushroom contains beta-glucans, polysaccharides known for their immunomodulatory properties and potential cognitive benefits. Beta-glucans may help regulate immune function and reduce inflammation in the brain, which could indirectly support cognitive function and mood regulation in individuals with ADHD.
Read more on Lion’s Mane Mushroom and their benefits here
Incorporating Lion's Mane Mushroom into ADHD Management
While research on Lion's Mane Mushroom's specific effects on ADHD is still in its early stages, its neuroprotective and cognitive-enhancing properties suggest potential benefits for individuals with ADHD.
As part of a comprehensive treatment approach, Lion's Mane Mushroom may complement existing interventions by supporting cognitive function and neuroplasticity.
However, further research, including clinical trials focusing specifically on ADHD populations, is needed to elucidate the efficacy and optimal dosing of Lion's Mane Mushroom in ADHD management.
Conclusion
ADHD is a multifaceted condition that necessitates a holistic approach to diagnosis and management. By understanding its symptoms, causes, and treatment options, we can empower individuals with ADHD to lead fulfilling lives.
Additionally, emerging complementary therapies like Lion's Mane Mushroom offer exciting avenues for further exploration and potential adjunctive support in ADHD management.
As research continues to elucidate the role of Lion's Mane Mushroom in neurological health, integrating evidence-based practices with innovative approaches holds promise for enhancing outcomes and promoting well-being in individuals with ADHD.
If you suspect that you or someone you know may have ADHD, seek professional evaluation and support to embark on a journey toward effective symptom management and holistic well-being.
Disclaimer: It's important to include a disclaimer stating that the information provided is for informational purposes only and should not be construed as medical advice. Always consult with a licensed physician or qualified healthcare professional before starting any new treatments or supplements, particularly if you have any underlying health conditions or are taking medications.
References
General ADHD Information
American Psychiatric Association. (2013). Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders (5th ed.). https://www.psychiatry.org/psychiatrists/practice/dsm
Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD). (2023, November 10). National Institute of Mental Health. https://www.nimh.nih.gov/health/topics/attention-deficit-hyperactivity-disorder-adhd
Causes of ADHD
Faraone, S. V., & Mick, E. (2015). Genetics of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder. Child and Adolescent Psychiatric Clinics of North America, 24(2), 351-368. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/20159345/
Shaw, P., Eckstrand, M., Sharp, W., Blumenthal, J., Wallace, E., & Leroupt, M. (2006). Structural and functional abnormalities in the frontal cortex of young adults with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Biological Psychiatry, 59(10), 942-949. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/18024590/
Barkley, R. A. (2006). Attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD): A handbook for diagnosis and treatment (3rd ed.). Guilford Publications.
Treatment Approaches for ADHD
Treatment of ADHD. (2023, November 10). National Institute of Mental Health. https://www.nimh.nih.gov/health/topics/attention-deficit-hyperactivity-disorder-adhd
Subcommittee on Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder, Steering Committee on Quality Improvement and Management, American Academy of Pediatrics. (2011). Clinical practice guideline for the diagnosis, evaluation, and treatment of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder in children and adolescents. Pediatrics, 128(5), e1074-e1146. https://publications.aap.org/pediatrics/article/144/4/e20192528/81590/Clinical-Practice-Guideline-for-the-Diagnosis
Lion's Mane Mushroom and ADHD
Lion's Mane Mushroom and Its Effects on Cognitive Function, Inflammation, and Other Health Aspects. (2022, December 23). National Institutes of Health. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24266378/

